Description
Active Ingredient
This medication is composed of the main active ingredient Acetazolamide. This main component belongs to a group of medicines known as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. It is a reversible inhibitor of the carbonic anhydrase enzyme. That leads to a reduction of hydrogen ion secretion at the renal tubule and increased renal excretion of sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, and water. This medication can be used as a diuretic or for the treatment of glaucoma. It works to prevent excessive build-up of aqueous humor. It inhibits carbonic anhydrase in the central nervous system to minimize abnormal and excessive discharge from CNS neurons. It is recommended in people with metabolic alkalosis to promote the retention of hydrogen ions at the level of the renal tubule.
Indications
Mentioned medication is approved to prevent and reduce the symptoms of altitude sickness. It can reduce headache, tiredness, nausea, dizziness, and shortness of breath that can occur at high altitudes generally above 10,000 feet/3,048 meters. It is specifically useful in situations when an individual cannot make a slow ascent. It is also indicated for the treatment of high pressure inside the eye due to certain types of glaucoma. It reduces the production of fluid inside the eye and decreases the buildup of body fluids caused by heart failure or certain medications.
Action Mechanism
The active component Acetazolamide inactivates carbonic anhydrase and interferes with the sodium pump, for the reduction of Intraocular pressure. This leads to a reduction in aqueous humor formation and thus lowering of IOP occurred. Diamox shows systemic effects that include increased renal loss of sodium, potassium, and water secondary to the drug’s renal tubular effects. Due to this arterial blood gases might show mild hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
Dosages
The medicine is recommended to reduce altitude sickness. Diamox dosage is as follows:
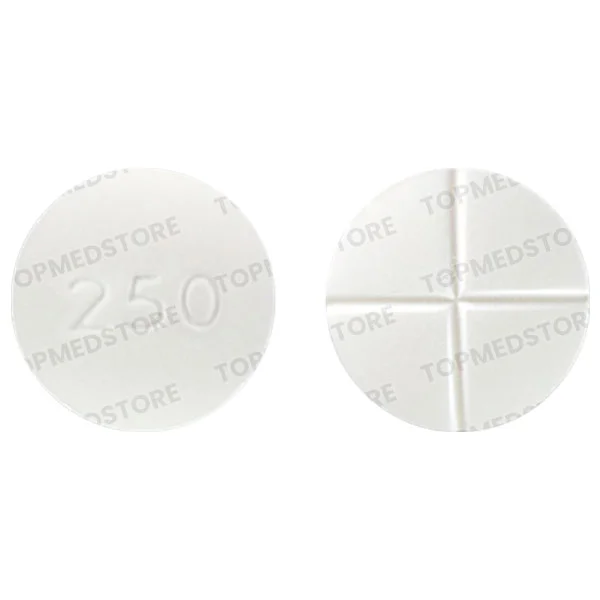
- 250 mg: This tablet must be taken 1 to 4 times a day exactly as prescribed by the doctor.
Generic Diamox Uses
- Acute Mountain Sickness
- Edema
- Seizure Prophylaxis
- Glaucoma
Who Should Not Take Diamox?
People with certain health conditions should not take Diamox.
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Poor kidney function
- Liver disease
- Emphysema
Common Side Effects
- Dizziness
- Increased urination
- Dry mouth
- Blurred vision
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Increased blood sugar
- Increased sensitivity to the sun
Rare Side Effects
- Ringing in the ears
- Hearing loss
- Increased body hair
- Persistent nausea and vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain
Severe Side Effects
- Easy bleeding or bruising
- Infections
- Mood changes or difficulty concentrating
- Palpitations or rapid heartbeat
- Severe muscle cramping
- Jaundice
Note
This medicine can be taken with or without food. It is advisable to drink plenty of fluids unless otherwise directed by the doctor. The dosage is based on the medical condition and response to treatment.
What is Diamox?
Acetazolamide is a strong carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
Why is Diamox prescribed to patients?
Acetazolamide is a prescription medicine used for the following conditions: To remove extra fluid from the body (diuresis) for people with heart failure Prevention and treatment of mountain sickness (altitude sickness) Seizures Glaucoma
What is the dosage for Diamox?
The usual recommended dose for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma ranges from 250 mg to 1 gram of acetazolamide per day.
Which drugs or supplements interact with Diamox?
Diamox should not be used with other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors like methazolamide (Neptazane). Use of two carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as it might cause dangerously low levels of blood potassium (hyponatremia).
What happens if the dose is missed?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up for the missed dose.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.